# The Ultimate Guide to Traceability Supply Chain: 5 Steps to Build a Transparent Future
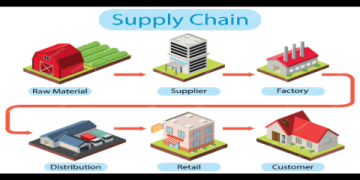
Imagine a customer scans a QR code on a steak package. Instantly, they see the calf’s birth farm, the feed it ate, the journey to the processing plant, and the final trip to the store shelf. This is not science fiction. This is the power of a modern traceability supply chain. It is the digital thread that connects every step of a product’s journey, from raw material to end consumer. For businesses today, it has shifted from a nice-to-have to a non-negotiable pillar of resilience, trust, and competitive advantage.
A traceability supply chain is a system that enables the tracking and documentation of a product’s history, location, and application across the entire supply chain. It answers critical questions: Where did this component come from? Who handled it? What were the storage conditions? In an era of heightened consumer awareness, complex global networks, and stringent regulations, lacking this visibility is a significant business risk.
## Why Traceability Is No Longer Optional
The drive for supply chain traceability is fueled by powerful external forces. Consumers are demanding more. A 2023 study by the IBM Institute for Business Value found that 77% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for brands that provide full transparency and sustainability. (来源: IBM Institute for Business Value). Regulatory pressure is mounting. Laws like the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), the EU’s Digital Product Passport, and Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act mandate a new level of disclosure.
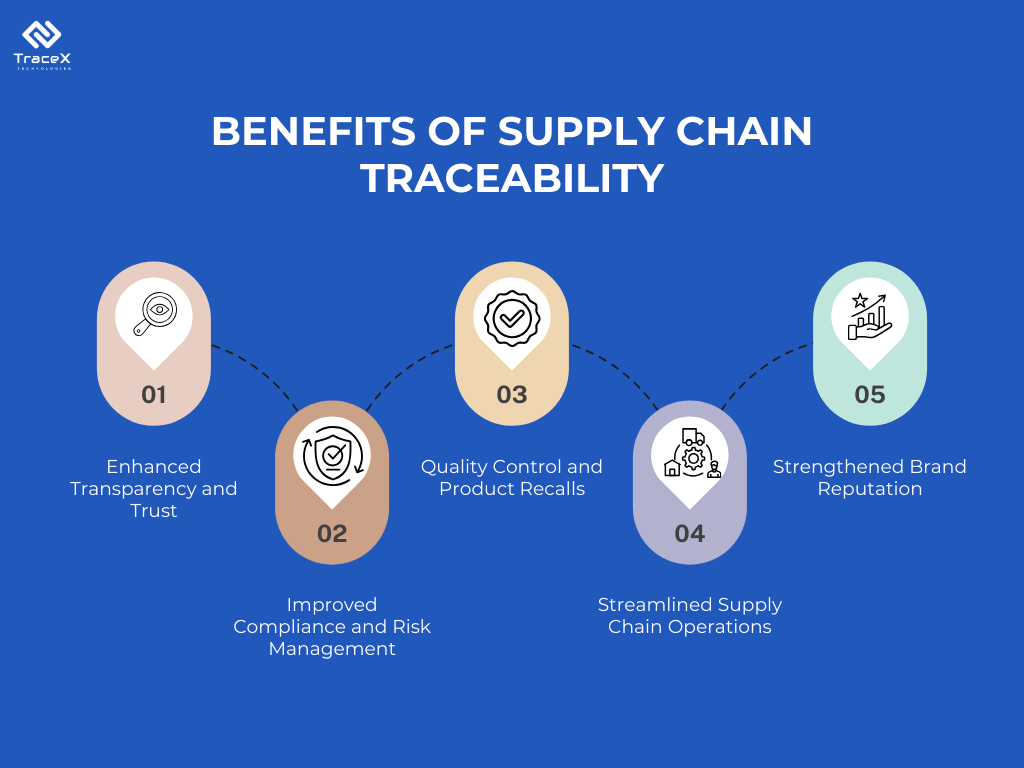
Furthermore, operational efficiency depends on it. Without traceability, a recall can become a nightmare, costing millions and destroying brand reputation. Conversely, a robust system can pinpoint an issue to a specific batch in minutes, limiting damage and cost. It also combats counterfeiting, ensures ethical sourcing, and provides the data needed to optimize logistics and reduce waste.
## Core Technologies Powering Modern Traceability
Building an end-to-end traceable supply chain relies on a stack of interconnected technologies. Each plays a unique role in capturing, storing, and sharing data.
BLOCKCHAIN creates an immutable, decentralized ledger. Once data is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing a single source of truth that all parties can trust without a central authority. INTERNET OF THINGS (IoT) sensors are the data collectors. They monitor conditions like temperature, humidity, and shock in real-time throughout transit. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and QR codes are the unique identifiers attached to products or pallets, allowing for rapid, non-line-of-sight scanning at each checkpoint.
These technologies feed data into a central platform, often cloud-based, which analyzes the information and provides actionable insights through dashboards. The synergy of these tools transforms a linear chain into a transparent, intelligent network.
## Traceability in Action: Industry Use Cases
The application of traceability supply chain solutions varies by sector but shares a common goal: verifiable proof.
In FOOD AND BEVERAGE, it ensures safety and provenance. Companies can track produce from farm to fork, verifying organic claims or fair-trade certifications. In PHARMACEUTICALS, it is critical for patient safety, preventing the infiltration of counterfeit drugs and ensuring proper storage of temperature-sensitive vaccines. The APPAREL industry uses it to validate sustainable and ethical sourcing of materials, appealing to conscious consumers. In MANUFACTURING, especially for automotive or aerospace, it provides a complete lineage for every component, which is vital for quality control and rapid recall if a specific part is found defective.
## Choosing Your Traceability Solution: A Comparative Guide
Not all traceability platforms are created equal. Your choice depends on your industry, complexity, and budget. Here is a comparison of two common approaches:
| Feature / Aspect | Blockchain-Based Platform | Centralized Cloud Platform |
|---|---|---|
| DATA INTEGRITY | Extremely High. Immutable ledger prevents tampering. | High, but relies on system and administrator security. |
| COLLABORATION | Excellent for multi-party networks. All participants access the same verified data. | Can be complex. Data sharing often requires custom integrations and trust in the data provider. |
| IMPLEMENTATION COST & COMPLEXITY | Generally higher upfront cost and technical complexity. | Typically lower initial barrier to entry, faster to deploy. |
| BEST SUITED FOR | Industries requiring ultimate trust & auditability (e.g., diamond trading, high-value pharmaceuticals, multi-tier sustainable sourcing). | Companies focusing on internal efficiency, recall management, and single-brand transparency. |
## A 5-Step Blueprint to Implement Your Traceability Supply Chain
Starting a traceability journey can seem daunting. Break it down into manageable phases with this actionable guide.
STEP 1: DEFINE SCOPE AND OBJECTIVES. Begin with a clear “why.” Are you aiming to comply with a new regulation, respond to a consumer demand, or solve a specific operational pain point like recall speed? Start with a single, high-impact product line or component rather than your entire catalog.
STEP 2: MAP YOUR SUPPLY CHAIN NETWORK. You cannot track what you do not know. Identify all entities involved: raw material suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, warehouses, and distributors. Understand the physical and information flows between them. This step often reveals surprising complexities and hidden risks.
STEP 3: SELECT KEY DATA POINTS AND TECHNOLOGY. Determine what data is critical to track. For food, it might be batch ID, origin farm, and temperature logs. For a manufactured good, it could be material certificates, assembly dates, and quality check results. Then, choose the identification technology (QR codes, RFID) and data platform that best fits your needs from the comparison above.
STEP 4: ESTABLISH DATA CAPTURE AND SHARING PROTOCOLS. Work with your partners to standardize how data is captured at each node. This is where collaboration is key. Define data formats, required fields, and the triggers for when data must be logged. Ensure the process is as automated as possible to avoid human error.
STEP 5: INTEGRATE, TEST, AND COMMUNICATE. Integrate the traceability data into your business systems like ERP or CRM. Run a pilot program with a willing partner to test the flow end-to-end. Finally, communicate the new capability to your customers. Use the traceability story in your marketing to build brand loyalty and trust.
## Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
WARNING: DO NOT UNDERESTIMATE THE HUMAN AND PARTNER ELEMENT. The most advanced technology will fail if people do not use it correctly or if suppliers refuse to participate. A traceability supply chain is a collaborative ecosystem. From my experience consulting with manufacturing clients, the biggest hurdle is often not the tech, but getting alignment and buy-in from long-standing partners who may be resistant to change or transparency. Start conversations early, frame it as a mutual benefit, and consider phased onboarding.
Another major mistake is treating traceability as a mere compliance checkbox. This mindset leads to minimal, siloed systems. Instead, view it as a strategic asset. The data you collect can reveal inefficiencies in your logistics, provide insights into supplier performance, and become a powerful tool for customer engagement and product innovation.
## Your Traceability Implementation Checklist
Before you launch your initiative, use this practical checklist to ensure you are on the right path. Remember, perfection is the enemy of progress. Start small, learn, and scale.
IDENTIFY A CLEAR BUSINESS DRIVER AND SET MEASURABLE GOALS.
MAP AT LEAST TWO TIERS OF YOUR SUPPLY CHAIN FOR THE PILOT PRODUCT.
SELECT DATA POINTS THAT DIRECTLY SUPPORT YOUR GOALS (E.G., CERTIFICATIONS, LOCATION, TEMPERATURE).
CHOOSE A TECHNOLOGY STACK BASED ON BUDGET, COMPLEXITY, AND PARTNER READINESS.
SECURE AGREEMENT FROM KEY PILOT PARTNERS BEFORE TECHNICAL DEPLOYMENT.
DESIGN A SIMPLE, CONSUMER-FACING OUTPUT (E.G., A WEBPAGE OR QR SCAN RESULT).
PLAN HOW YOU WILL USE THE COLLECTED DATA INTERNALLY FOR PROCESS IMPROVEMENT.
ALLOCATE BUDGET FOR PARTNER TRAINING AND ONGOING SYSTEM MAINTENANCE.
The journey to a fully traceable supply chain is a strategic evolution. It builds a foundation of resilience that protects your brand, delights your customers, and unlocks new levels of operational intelligence. The question is no longer if you should invest in traceability, but how quickly you can start.