# The Ultimate Guide to RPA in Supply Chain: 7 Ways to Automate for Efficiency
The modern supply chain is a complex web of data, processes, and people. Manual tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and order tracking are not just slow. They are expensive and prone to human error. This is where Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, becomes a game-changer. RPA in supply chain management uses software robots to mimic human actions on digital systems. These bots can work 24/7, executing rule-based tasks with perfect accuracy. The result is a supply chain that is faster, cheaper, and more reliable.
This guide will explain exactly how RPA transforms supply chain operations. We will explore key use cases, provide a step-by-step implementation plan, and show you how to avoid common pitfalls. Let us dive into the world of automated logistics.
UNDERSTANDING RPA AND ITS SUPPLY CHAIN APPLICATIONS
At its core, RPA is not a physical robot. It is a software application. You can think of it as a digital worker that logs into applications, moves files, copies and pastes data, fills in forms, and performs other repetitive tasks. In the supply chain context, these tasks are everywhere.
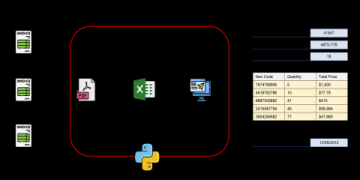
The primary value of RPA supply chain automation lies in connecting disparate systems without costly and time-consuming integration projects. For instance, a bot can take an order from an email or a PDF, extract the relevant details, and input them directly into an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system like SAP or Oracle. This bridges gaps between legacy systems and modern platforms seamlessly.
KEY AREAS WHERE RPA DRIVES SUPPLY CHAIN VALUE
Procurement and Order Processing
The journey often starts with procurement. RPA bots can automate purchase order creation, send them to suppliers, and track acknowledgments. When orders arrive, bots can match packing slips, purchase orders, and invoices. This three-way matching, a traditionally labor-intensive process, can be completed in minutes instead of hours, accelerating payment cycles and improving supplier relationships.
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Visibility into inventory levels is critical. RPA can automatically update inventory records across multiple systems as goods are received, picked, packed, or shipped. Bots can monitor stock levels in real-time and generate replenishment alerts when thresholds are breached. This prevents both stockouts and overstocking, optimizing working capital. A study by Deloitte found that companies using automation in their supply chains see a 30% reduction in operational costs (source: Deloitte Insights).
Logistics and Shipping
Coordinating shipments involves constant communication with carriers, tracking shipments, and updating customers. RPA can automate carrier selection based on predefined rules (cost, speed), generate shipping labels and documentation, and provide real-time tracking updates to internal systems and customers. This reduces manual follow-ups and improves delivery transparency.
Finance and Compliance
Beyond operations, RPA streamlines back-office finance tasks in the supply chain. This includes automated invoice processing, accounts payable/receivable reconciliation, and generating compliance reports. Bots ensure data accuracy for audits and can flag discrepancies for human review.
COMPARING RPA TOOLS FOR SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Choosing the right RPA platform is crucial. Here is a comparison of two leading approaches: a dedicated enterprise platform and a more agile, modern solution.
| Feature / Aspect | Enterprise RPA Platform (e.g., UiPath, Automation Anywhere) | Modern Automation Platform (e.g., Microsoft Power Automate, low-code tools) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | High-volume, complex, back-end processes across legacy systems. | Rapid development, strong integration with modern cloud apps (Office 365, Dynamics). |
| Best For | Large-scale, centralized automation of core supply chain transactions (e.g., full PO-to-pay cycle). | Departmental or team-level automation, quick workflow fixes, and citizen developer initiatives. |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher. Often requires specialized developers and a Center of Excellence (CoE). | Lower. More user-friendly with drag-and-drop interfaces, faster to deploy. |
| Cost Structure | Typically higher licensing fees, based on bots or workloads. | Often subscription-based, sometimes included in broader software suites. |
A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO IMPLEMENTING RPA IN YOUR SUPPLY CHAIN
Based on my experience guiding teams through this journey, a methodical approach is key to success. Do not try to automate everything at once.
Step 1: Process Identification and Assessment
Begin by mapping your supply chain processes. Look for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, high-volume, and prone to error. Prime candidates include data entry from PDFs or emails, report generation, and system-to-system data transfers. Involve the employees who do these tasks daily. They know the pain points best.
Step 2: Prioritize and Select a Pilot Process
Choose a process that is clearly defined, stable, and has a measurable return on investment. A good pilot might be automating the entry of supplier invoices into your accounting system. A successful, small-scale project builds confidence and secures buy-in for broader initiatives.
Step 3: Choose Your RPA Tool and Team
Select a tool that fits your technical expertise and budget, as highlighted in the comparison table. Assemble a small team with a process expert and a developer. Many organizations now establish a Center of Excellence to govern automation efforts.
Step 4: Develop, Test, and Refine the Bot
The developer will build the bot, while the process expert validates each step. Test the bot thoroughly in a controlled environment with historical data. Expect to refine the logic. The goal is 100% accuracy before go-live.
Step 5: Deploy, Monitor, and Scale
Launch the bot to work alongside humans initially. Monitor its performance and exception rates closely. Once stable, you can scale by adding more bots or automating adjacent processes. According to Gartner, by 2025, 80% of supply chain interactions will happen across cloud-based platforms, making RPA integration even more vital (source: Gartner).
COMMON PITFALLS AND HOW TO AVOID THEM
WARNING: AVOID THESE RPA IMPLEMENTATION MISTAKES
A major pitfall is automating a broken process. RPA will simply do the wrong thing faster. Always optimize the process first, then automate. Another common error is neglecting change management. Employees may fear job loss. Communicate that RPA is a tool to eliminate mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on higher-value work like analysis, supplier relationship management, and problem-solving. Finally, do not underestimate maintenance. Processes and underlying applications change. Your bots need monitoring and updates to remain effective.
FUTURE OF RPA: INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN
The next evolution is combining RPA with artificial intelligence and machine learning. This is often called Intelligent Process Automation (IPA). Imagine a bot that not only extracts data from an invoice but also uses AI to understand unstructured text, make decisions on non-standard line items, and learn from corrections. This moves automation from simple tasks to complex cognitive processes, further enhancing supply chain resilience and intelligence.
FINAL CHECKLIST FOR RPA SUPPLY CHAIN SUCCESS
To ensure your automation journey is successful, use this practical checklist.
IDENTIFY a high-volume, rule-based supply chain process.
CALCULATE the potential ROI in time and cost savings.
SECURE executive sponsorship and team buy-in.
SELECT the appropriate RPA tool for your needs and scale.
OPTIMIZE the process before you begin to automate it.
START with a controlled pilot project.
DOCUMENT everything clearly for maintenance and scaling.
TRAIN your staff to work with and manage the new digital workforce.
MEASURE results against your initial goals.
PLAN for ongoing bot maintenance and process evolution.
By following this guide, you can harness the power of RPA to build a supply chain that is not just efficient, but truly intelligent and competitive. The transformation starts with a single, automated process.