# The Ultimate Guide to Gen AI in Supply Chain: 5 Game-Changing Applications and How to Start
The modern supply chain is a complex web of data, decisions, and disruptions. Traditional software, while powerful, often struggles with prediction, adaptation, and creative problem-solving. This is where generative AI in supply chain management is emerging as a transformative force. Unlike analytical AI that interprets data, generative AI creates new content, scenarios, and strategies. It is not just about seeing patterns; it is about generating optimal paths forward. For leaders, understanding and implementing gen AI in supply chain operations is shifting from a competitive edge to a business imperative.
This guide will explore the practical applications, tangible benefits, and a clear roadmap for integrating this technology. We will move beyond the hype to deliver actionable insights.
## What is Generative AI and How Does It Differ in Supply Chain?
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models, like large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models, that can generate new, original outputs. These outputs can be text, code, images, or complex data simulations. In a supply chain context, this capability is revolutionary.
Traditional supply chain AI is predictive. It answers questions like, “What is the expected demand for this product?” or “When will this shipment arrive?” Generative AI, however, is prescriptive and creative. It answers questions like, “Generate five optimal delivery routes considering real-time traffic, weather, and carbon goals,” or “Draft a supplier negotiation email based on current market volatility and our contract history.” It synthesizes vast amounts of structured and unstructured data to propose novel solutions a human might not immediately conceive.
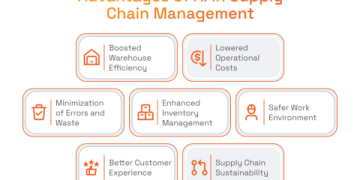
## Five Transformative Applications of Gen AI in Supply Chain
The potential use cases are vast. Here are five areas where generative AI is delivering concrete value.
1. DYNAMIC DEMAND PLANNING AND FORECASTING: Moving beyond statistical models, gen AI can incorporate unstructured data signals—news about geopolitical events, social media sentiment, weather patterns, even competitor announcements—to generate more nuanced and multi-scenario demand forecasts. It can create “what-if” narratives for different economic conditions.
2. INTELLIGENT INVENTORY OPTIMIZATION: Gen AI models can generate optimal stock-level recommendations for thousands of SKUs across numerous locations. They can simulate the impact of promotions, supply delays, or sudden demand spikes to propose rebalancing strategies, minimizing both stockouts and excess capital tied up in inventory.
3. AUTOMATED SUPPLIER COMMUNICATION AND RISK MANAGEMENT: Gen AI can draft and personalize RFPs, contracts, and routine communication. More critically, it can continuously scan news, financial reports, and geopolitical databases to generate supplier risk profiles and early-warning alerts, proposing alternative sourcing strategies.
4. GENERATIVE LOGISTICS AND ROUTE OPTIMIZATION: This goes beyond finding the shortest path. AI can generate holistic logistics plans that balance cost, speed, sustainability (carbon footprint), and reliability. It can create contingency routes in real-time and automatically generate customs documentation or carrier communications.
5. ENHANCED CUSTOMER SERVICE AND ORDER MANAGEMENT: AI-powered chatbots and interfaces can handle complex, multi-step customer inquiries about orders, returns, and product availability. They can generate personalized status updates and proactively suggest solutions for potential delivery delays.
To illustrate the functional differences between generative AI and traditional tools in key areas, consider the following comparison.
| Supply Chain Function | Traditional/Analytical AI Approach | Generative AI Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Demand Planning | Analyzes historical sales data to produce a numerical forecast. | Generates multiple forecast scenarios by synthesizing historical data, market news, and social trends into descriptive narratives. |
| Risk Management | Flags a supplier based on a financial score threshold. | Generates a summarized risk report with cited sources and proposes a ranked list of alternative suppliers with justification. |
| Logistics Management | Calculates the most fuel-efficient route based on distance. | Generates a holistic transport plan optimizing for cost, time, carbon emissions, and driver schedules, including draft delivery notifications. |
## A Step-by-Step Guide to Pilot Generative AI in Your Supply Chain
Implementing generative AI does not require a full-scale, company-wide overhaul overnight. A focused pilot project is the most effective path. Here is a practical, five-step guide to get started.
STEP 1: IDENTIFY A HIGH-IMPACT, CONTAINED USE CASE. Do not start with your most complex global network. Choose a specific pain point with clear metrics. Examples include: automating the generation of weekly inventory reports for a single warehouse, or creating draft responses for a common category of supplier emails.
STEP 2: AUDIT AND PREPARE YOUR DATA. Generative AI models require quality data. Gather the relevant structured data (inventory levels, order history) and identify sources of unstructured data (email threads, supplier contracts, logistics notes). Ensure data is clean and accessible.
STEP 3: SELECT THE RIGHT TOOL OR PLATFORM. You have options: using API-based foundation models (like OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Google’s Gemini), adopting a specialized supply chain AI platform (like Blue Yonder, Coupa, or emerging startups), or developing a custom solution. For most pilots, a platform or API approach is most feasible.
STEP 4: DEVELOP, TEST, AND REFINE WITH DOMAIN EXPERTS. Build your initial application, such as a chatbot for logistics queries or a report generator. CRUCIALLY, involve your supply chain planners and logistics managers in testing. Their feedback is essential to refine the AI’s outputs for accuracy and practical relevance.
STEP 5: MEASURE, SCALE, AND ITERATE. Define success metrics for your pilot: time saved, reduction in errors, cost avoided. With proven results, you can plan to scale the application to other regions or functions, continuously iterating based on user feedback.
## Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
WARNING: AVOIDING THESE MISTAKES IS CRITICAL FOR SUCCESS.
A major pitfall is treating generative AI as a magic box that requires no human oversight. The technology is powerful but not infallible. It can produce convincing but incorrect or nonsensical outputs—a phenomenon known as “hallucination.” Always implement a human-in-the-loop (HITL) review process, especially for critical decisions like contract generation or high-value logistics changes.
Another common error is neglecting change management. Your team may fear job displacement. Frame gen AI as a powerful co-pilot that automates tedious tasks, freeing them for higher-value strategic work like relationship management and exception handling. Training and transparent communication are non-negotiable.
Furthermore, data privacy and security are paramount. Ensure any platform or model you use complies with your industry’s regulations. Do not input sensitive supplier contracts or proprietary cost data into a public, unsecured AI model without proper safeguards.
## The Tangible Business Impact and Future Outlook
The business case is strong. A recent study by McKinsey estimated that generative AI could add $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually across just 63 business use cases, with a significant portion coming from supply chain and manufacturing functions (来源: McKinsey & Company). In our team’s experience working with early adopters, the most immediate gains are in productivity—planners reclaiming 20-30% of their time from manual reporting—and in resilience, as AI-generated scenarios help companies react faster to disruptions.
Looking ahead, the integration of gen AI in supply chain will deepen. We will see the rise of autonomous supply chain agents that not only recommend actions but execute them within defined parameters—like autonomously rerouting shipments or placing micro-orders with suppliers. The fusion of generative AI with digital twins (virtual models of the physical supply chain) will enable unprecedented simulation and planning capabilities.
Getting started now positions your organization to lead in this new era. The goal is not to replace human expertise but to augment it with a powerful, generative intelligence that can navigate complexity and unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation.
IMPLEMENTATION CHECKLIST FOR GEN AI IN SUPPLY CHAIN:
– Identify one specific, measurable pilot use case.
– Assure data quality and accessibility for the pilot.
– Choose an implementation path: API, specialized platform, or custom build.
– Establish a human-in-the-loop review protocol for all AI outputs.
– Develop a change management and training plan for affected staff.
– Define clear KPIs to measure the pilot’s success (e.g., time saved, error reduction).
– Prioritize data security and vendor compliance checks.
– Plan an iteration and scaling roadmap based on pilot results.