# The Ultimate Guide to Advanced Supply Chain Management: 7 Key Components for 2024
Modern business is a battle fought on the logistics front. An advanced supply chain is no longer a luxury for multinational giants. It is the critical backbone for any company aiming to survive volatility, meet soaring customer expectations, and unlock new profit margins. But what exactly transforms a traditional supply chain into an advanced one? This guide breaks down the core components, technologies, and strategies that define a truly modern, resilient, and intelligent supply network.
At its heart, an advanced supply chain leverages data, automation, and interconnected processes to create visibility, agility, and efficiency from the supplier’s supplier to the end customer. It moves beyond simple linear models to a dynamic, networked ecosystem.
## The Foundational Shift: From Linear Chains to Intelligent Networks
The old model of a supply chain was a sequential, often siloed process: procure, make, move, sell. Information flowed slowly, and disruptions caused major delays. An advanced supply chain flips this script. It operates as a synchronized network where data is shared in real-time across all partners. This shift is powered by digital integration, allowing for predictive rather than reactive management. The goal is end-to-end visibility, where you can track a component from its raw material state to its installation in a finished product at a customer’s location.
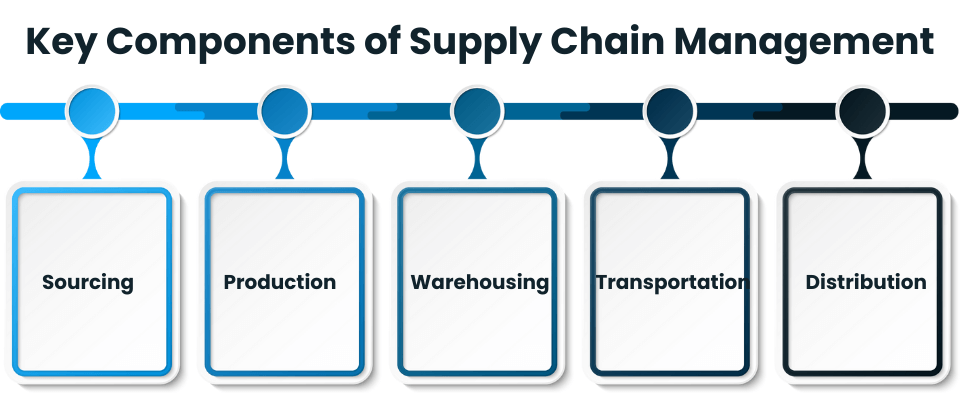
## Core Components of an Advanced Supply Chain
Building this capability requires integrating several key technological and strategic pillars.
1. DATA ANALYTICS AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: This is the brain of the operation. Advanced analytics processes vast amounts of data from IoT sensors, ERP systems, and market feeds. AI and machine learning algorithms use this data to predict demand more accurately, optimize inventory levels, identify potential disruptions, and suggest optimal shipping routes. For instance, a study by McKinsey found that companies using AI in their supply chains have improved logistics costs by 15%, inventory levels by 35%, and service levels by 65%. (来源: McKinsey & Company)
2. INTERNET OF THINGS AND REAL-TIME VISIBILITY: IoT sensors on containers, vehicles, and warehouse shelves provide a constant stream of real-time data. This enables true visibility into the location, condition (like temperature or humidity), and status of goods in transit. No more guessing where a shipment is or if perishable goods have spoiled.
3. ADVANCED AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICS: In warehouses, this means autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and smart picking systems. These technologies drastically increase speed, accuracy, and safety while reducing labor costs in repetitive tasks. Beyond the warehouse, automation extends to robotic process automation (RPA) for administrative tasks like order processing and invoice reconciliation.
4. INTEGRATED PLANNING AND EXECUTION SYSTEMS: Siloed software creates blind spots. An advanced supply chain relies on platforms that integrate planning (like demand forecasting, inventory planning) with execution (like warehouse management, transportation management). This creates a single source of truth and allows for dynamic re-planning when conditions change.
5. SUPPLY CHAIN RESILIENCY AND RISK MANAGEMENT: Recent global events have made this component non-negotiable. An advanced supply chain proactively maps its entire supplier network, identifies single points of failure, and develops mitigation strategies. This includes diversifying suppliers, holding strategic buffer stock for critical items, and using digital twins to simulate and prepare for disruption scenarios.
6. SUSTAINABILITY AND CIRCULARITY: Modern consumers and regulators demand ethical and environmentally responsible practices. Advanced supply chains embed sustainability into their DNA. This involves optimizing routes to reduce carbon emissions, selecting green suppliers, designing products for easier recycling, and implementing circular economy principles to reuse materials.
7. COLLABORATIVE PARTNER ECOSYSTEMS: No company is an island. Advanced networks thrive on deep collaboration with suppliers, logistics providers, and even customers. Sharing data and forecasts through secure portals or blockchain-ledger systems builds trust and enables the entire network to align and respond faster to changes.
## Technology Showdown: Key Enablers Compared
While many technologies contribute, some are fundamental catalysts. Here is a comparison of two pivotal technologies in building an advanced supply chain.
| Technology | Primary Role in Advanced Supply Chain | Key Benefits | Implementation Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning | The predictive brain for forecasting, optimization, and prescriptive insights. | Demand prediction, automated decision-making, dynamic pricing, predictive maintenance. | Requires high-quality, clean data and significant upfront investment in talent and infrastructure. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | The central nervous system providing real-time sensory data from physical assets. | Real-time tracking, condition monitoring, asset utilization, enhanced security. | Involves deploying and maintaining a vast sensor network and managing massive data streams. |
## A 5-Step Roadmap to Begin Your Advanced Supply Chain Journey
Transitioning does not happen overnight. Based on my experience consulting with mid-sized manufacturers, a pragmatic, phased approach yields the best results. Here is a practical starting roadmap.
STEP 1: CONDUCT A MATURITY ASSESSMENT. Honestly evaluate your current supply chain. Map your key processes, identify data silos, and pinpoint your biggest pain points (e.g., stockouts, high logistics costs, poor forecast accuracy). This baseline is crucial.
STEP 2: PRIORITIZE A SINGLE, HIGH-IMPACT USE CASE. Do not try to boil the ocean. Select one area where advanced technology can solve a clear business problem. A common and impactful starting point is implementing demand sensing with basic analytics to improve forecast accuracy for your top 20% of SKUs.
STEP 3: INVEST IN DATA FOUNDATION AND INTEGRATION. Garbage in, garbage out. Ensure your data from ERP, WMS, and other systems is clean, standardized, and accessible. Often, the first project is creating a centralized data lake or warehouse.
STEP 4: PILOT A TECHNOLOGY SOLUTION. Run a small-scale pilot for your chosen use case. For example, deploy IoT trackers on shipments for your most valuable or perishable product line. Measure the results in terms of reduced loss, improved customer notifications, and lower insurance costs.
STEP 5: SCALE AND ITERATE. Use the lessons and ROI from the pilot to build a business case for broader rollout. Then, move to the next priority use case, continually building on your digital foundation.
## Common Pitfall to Avoid: The Technology-First Trap
WARNING: A MAJOR MISSTEP COMPANIES MAKE IS CHASING SHINY NEW TECHNOLOGY WITHOUT A CLEAR BUSINESS PROBLEM TO SOLVE. They buy an AI platform or blockchain solution looking for a problem. This almost always leads to wasted investment and disillusionment. The correct sequence is always: Identify Business Pain Point > Define Desired Outcome > Select Supporting Process Change > Then Choose Enabling Technology. Technology is an enabler, not a strategy in itself.
## Real-World Impact and the Path Forward
The benefits of maturing your supply chain are tangible. Companies with advanced capabilities report significantly lower operating costs, stronger customer loyalty due to reliable service, and an enhanced ability to enter new markets. They are also better insulated from shocks. According to a report by Accenture, resilient companies with advanced supply chains lost less market share during disruptions and recovered 50% faster than their peers. (来源: Accenture)
From our team’s work, the most successful transformations are led from the top, with a clear vision that connects supply chain advancement to overall business strategy. It is a continuous journey of improvement, not a one-time project.
Interestingly, the next frontier is the autonomous supply chain, where systems will self-correct, self-optimize, and even negotiate with each other with minimal human intervention. The journey to an advanced supply chain is the essential preparation for that future.
## Your Advanced Supply Chain Implementation Checklist
To conclude, here is a concise checklist to guide your next steps. Use this as a practical reference.
– Completed a full assessment of current supply chain maturity and pain points.
– Defined and documented a clear business case with measurable ROI targets.
– Secured executive sponsorship and cross-functional team alignment.
– Audited and initiated cleanup of core master data (product, supplier, customer).
– Selected a pilot project focused on a specific, high-value problem.
– Chosen technology partners based on pilot needs and integration capability.
– Established key performance indicators to measure pilot success.
– Developed a change management plan for internal and partner teams.
– Created a phased roadmap for scaling successful pilots.
– Instituted a continuous review process to adapt to new technologies and market changes.