# The Ultimate Guide to the Automobile Value Chain: Components, Challenges, and Future Trends
The automobile value chain is the intricate network of activities that transforms raw materials into a finished vehicle and delivers it to the end customer. Understanding this chain is not just for industry insiders. For investors, policymakers, and even consumers, it reveals where value is created, where costs accumulate, and how the entire automotive ecosystem is being reshaped by technology. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the automobile value chain, its modern challenges, and the forces driving its future.
At its core, the automobile value chain can be segmented into a series of sequential and interconnected phases. These range from research and design all the way to after-sales service. Each link in this chain adds specific value and faces unique pressures. We will explore each stage in detail, but first, it is crucial to grasp the overarching model.
The traditional linear model is giving way to a more circular and interconnected system. Globalization, digitalization, and the shift to electric vehicles are the primary disruptors. For instance, the battery now accounts for a significant portion of an electric vehicle’s total cost, reshaping the entire upstream supply chain. According to a BloombergNEF report, the volume-weighted average price of a lithium-ion battery pack was $139 per kWh in 2023, a dramatic drop from over $1,200 in 2010, illustrating both progress and intense focus in this new critical component (来源: BloombergNEF).
## The Five Core Stages of the Automobile Value Chain
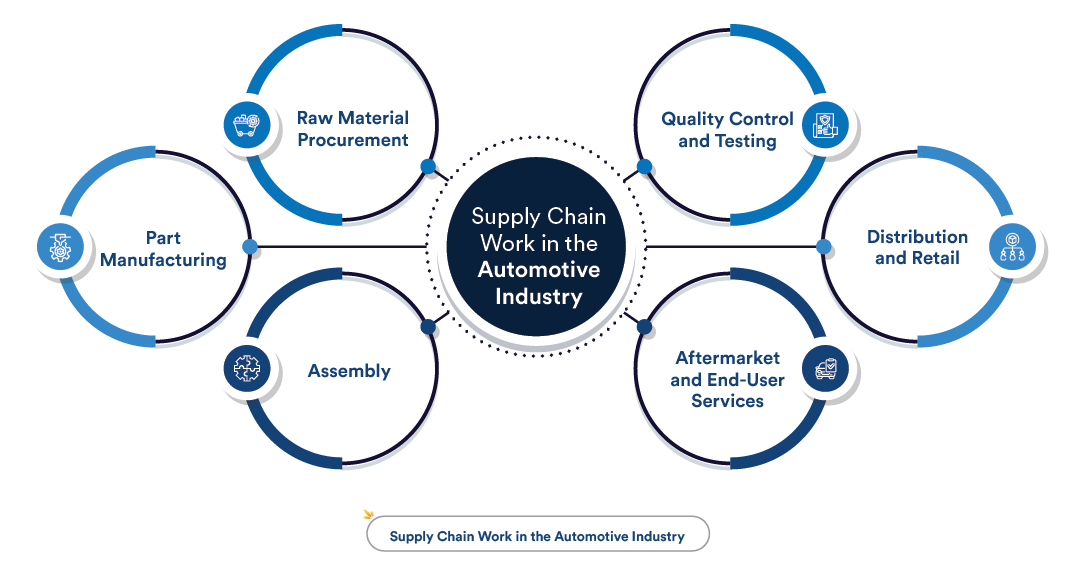
The journey of a car begins long before metal is stamped. We can break down the automobile value chain into five fundamental stages.
STAGE 1: RESEARCH, DEVELOPMENT, AND DESIGN (R&D)
This is the innovation engine. Billions are invested here in designing new models, engineering platforms, developing powertrains (especially electric and hybrid systems), and creating the software that defines modern vehicles. This phase sets the cost, performance, and feature parameters for everything that follows. It is increasingly software-centric, with lines of code becoming as important as mechanical blueprints.
STAGE 2: SUPPLY AND PRODUCTION OF PARTS & COMPONENTS
Here, thousands of suppliers, from tier-1 giants to specialized tier-3 firms, manufacture everything from microchips and infotainment screens to seats and axles. This segment of the automobile value chain is highly globalized and complex. Disruptions here, as seen during the semiconductor shortage, can halt entire production lines worldwide.
STAGE 3: VEHICLE ASSEMBLY AND MANUFACTURING
OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) like Toyota, Volkswagen, and Ford operate assembly plants where components converge to become a vehicle. This stage focuses on lean manufacturing, robotics, and quality control. The efficiency of this “final assembly” link is a major determinant of profitability.
STAGE 4: DISTRIBUTION, MARKETING, AND SALES
Once built, cars move through a logistics network to distribution centers and then to dealerships. Marketing builds demand, and the sales interface (increasingly online and direct) finalizes the transaction with the customer. This stage is undergoing massive change with the rise of digital retail and agency sales models.
STAGE 5: AFTER-SALES SERVICE AND END-OF-LIFE
Value creation does not stop at the sale. Maintenance, repairs, spare parts, and financing generate substantial, recurring revenue. At the end of its life, the vehicle enters the recycling and remanufacturing stream, a phase gaining importance due to sustainability mandates and the need to recover critical battery materials.
## The Digital Transformation: A New Layer in the Value Chain
A modern analysis of the automobile value chain must account for a new, parallel layer: digital services. This includes connected car data, over-the-air software updates, subscription features, and mobility-as-a-service platforms like ride-hailing. This digital layer creates ongoing revenue streams and deepens customer relationships beyond the one-time vehicle sale. It turns the car from a product into a connected platform.
## Critical Challenges and Disruptions
The automobile value chain is under stress from multiple angles. Supply chain fragility was exposed by recent global events. The transition to electric vehicles requires entirely new supplier relationships and raw material sourcing, such as for lithium and cobalt. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions are prompting regionalization, with companies building supply chains closer to home markets, a trend known as “nearshoring.”
Another major challenge is the talent shift. The industry now competes for software engineers and data scientists against tech giants, not just other automakers. This necessitates a cultural and operational transformation within traditional automotive companies.
## Software vs. Hardware: A Comparative Analysis
The increasing importance of software is fundamentally altering value distribution. Here is a comparative look at how these two pillars differ within the modern automobile value chain.
| ASPECT | HARDWARE (TRADITIONAL) | SOFTWARE (EMERGING) |
|---|---|---|
| VALUE DRIVER | Physical performance, durability, cost of materials. | User experience, features, data, connectivity, updates. |
| DEVELOPMENT CYCLE | Long (3-5 years for new model), iterative. | Short (agile, continuous), can be updated post-sale. |
| REVENUE MODEL | Primarily one-time sale at point of purchase. | Potential for recurring revenue (subscriptions, services). |
| KEY COMPETITORS | Other OEMs, tier-1 suppliers. | Tech companies (e.g., Google, Apple), software startups. |
| SUPPLY CHAIN RISK | Raw material scarcity, logistics disruption. | Cybersecurity threats, talent shortage, intellectual property. |
## How to Analyze a Company’s Position in the Automobile Value Chain: A 5-Step Guide
Whether you are an investor or a professional, evaluating a company’s role is key. Follow this operational guide.
STEP 1: IDENTIFY THE SEGMENT
Determine which of the five core stages the company operates in. Is it a raw material miner, a battery component supplier, an OEM, a dealership group, or a digital service provider?
STEP 2: ASSESS VERTICAL INTEGRATION
How much of the chain does the company control? A highly integrated OEM (making its own batteries and software) has different risks and opportunities than a specialized sensor manufacturer.
STEP 3: EVALUATE TECHNOLOGICAL DEPENDENCY
Analyze the company’s exposure to key technological shifts. For a supplier, this could be dependence on internal combustion engine parts versus electric drive components.
STEP 4: MAP KEY CUSTOMER AND SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIPS
Concentration risk is crucial. A supplier reliant on a single OEM is riskier than one with a diversified customer base. The same applies to sourcing critical materials.
STEP 5: ANALYZE MARGIN PROFILE AND BARRIERS TO ENTRY
Compare the company’s profit margins to its segment average. High margins often indicate strong technology or market position. Assess what protects those margins (e.g., patents, contracts, scale).
COMMON MISCONCEPTION TO AVOID
A frequent error is viewing the automobile value chain as static and purely linear. The most significant changes are happening in the interactions *between* stages. For example, software development (Stage 1) now requires continuous feedback from vehicle data (Stage 5). Circular flows of data, materials, and value are becoming the norm, making a rigid, one-way view obsolete.
## The Future: Electrification, Autonomy, and Circularity
The future automobile value chain will look radically different. Electrification shifts value upstream to battery production and mineral refining. Autonomous driving technology could redistribute value toward AI developers and mobility service operators. Most importantly, circular economy principles will close the loop, making end-of-life vehicle recycling and battery repurposing a major value-creation stage. Sustainability is transitioning from a cost center to a core competitive advantage.
In my experience consulting with automotive suppliers, the most successful firms are those proactively mapping their position not just in today’s chain, but in where the chain will be in five years. They are investing in partnerships, software capabilities, and sustainable processes to secure their role. The pace of change is unprecedented. A study by McKinsey & Company estimates that software could account for 30 percent of a vehicle’s value by 2030, up from about 10 percent today (来源: McKinsey & Company). This single statistic underscores the monumental shift underway.
The automobile value chain is more than a production flowchart. It is a dynamic battlefield where legacy industrial might clashes with digital disruption. Understanding its currents is essential for anyone connected to the future of mobility.
CHECKLIST FOR UNDERSTANDING THE AUTOMOBILE VALUE CHAIN
– Define the five core stages: R&D, Supply, Assembly, Distribution, After-Sales.
– Recognize the impact of electric vehicles on upstream supply and battery value.
– Identify the growing parallel layer of digital services and software.
– Analyze the comparative dynamics of hardware versus software value creation.
– Evaluate key disruption factors: supply chain fragility, talent shift, geopolitics.
– Assess a company’s strategic position using the five-step analysis guide.
– Look beyond the linear model to circular flows of data and materials.
– Monitor the convergence of sustainability and economic value in recycling.
– Track the redistribution of value toward software and new mobility services.
– Understand that the chain is a fluid ecosystem, not a fixed pipeline.