# The Ultimate Guide to Supply Chain Performance: Metrics, Strategies, and Expert Insights
Supply chain performance is the heartbeat of modern business. It determines how efficiently goods flow from raw materials to the end customer, impacting everything from cost and profit to customer satisfaction and brand reputation. In an era of global disruption and rising consumer expectations, mastering your supply chain performance is not just an operational goal. It is a critical competitive advantage.
This comprehensive guide will move beyond basic definitions. We will explore the core metrics that matter, actionable strategies for improvement, and the technology shaping the future. Whether you are a logistics manager or a business leader, this resource provides a clear roadmap to a more resilient and high-performing supply chain.
## Understanding Supply Chain Performance
At its core, supply chain performance measures how well your entire network of suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and transportation channels works together to fulfill customer demand. Think of it as a scorecard for your end-to-end operations. High performance means delivering the right product, to the right place, at the right time, and at the right cost.
The goal is to create a seamless, efficient, and adaptable flow. This requires balancing often competing priorities: speed versus cost, efficiency versus resilience, and standardization versus customization. A truly optimized supply chain performance strategy finds the sweet spot that aligns with your specific business objectives.
## The 5 Critical Metrics You Must Track
You cannot improve what you do not measure. Focusing on the wrong data is a common pitfall. Here are the five non-negotiable metrics for assessing supply chain performance.
1. Perfect Order Fulfillment: This is the ultimate measure of customer satisfaction. It calculates the percentage of orders delivered on time, in full, undamaged, and with accurate documentation. Industry leaders aim for rates above 95%.
2. Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time: This metric reveals your financial efficiency. It measures the days between paying for raw materials and receiving payment from the customer for the finished product. Shorter cycles free up working capital.
3. Inventory Days of Supply: This shows how long your inventory sits before being sold. While low levels reduce holding costs, too little stock risks shortages. The key is optimizing for demand.
4. Supply Chain Cost as a Percentage of Revenue: This provides a high-level view of operational efficiency. It includes all costs: procurement, production, warehousing, and transportation. Tracking this over time highlights the impact of your improvement efforts.
5. On-Time In-Full (OTIF) Delivery: A subset of perfect order, OTIF is crucial for retail and manufacturing partnerships. Major retailers often impose strict OTIF standards and financial penalties for non-compliance.
## A Strategic Framework for Improvement
Improving supply chain performance is a continuous journey, not a one-time project. Based on my experience working with mid-sized manufacturers, a structured approach yields the best results. The following framework can guide your efforts.
STEP 1: DIAGNOSE AND BASELINE. Conduct a thorough audit of your current end-to-end process. Map all touchpoints and collect data on the five key metrics above. Identify your three biggest pain points, such as chronic warehouse delays or unreliable supplier quality.
STEP 2: FOSTER COLLABORATION AND VISIBILITY. Siloed information is the enemy of performance. Implement shared platforms where key partners (suppliers, logistics providers) can update statuses. Even a shared dashboard can dramatically reduce communication delays and errors.
STEP 3: LEVERAGE TECHNOLOGY STRATEGICALLY. Do not buy software for its own sake. Identify tools that solve your diagnosed pain points. For inventory issues, consider demand forecasting software. For transportation delays, a real-time tracking solution might be the answer.
STEP 4: DEVELOP A RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN. A resilient supply chain is a high-performing one. Map your key dependencies and single points of failure. Develop contingency plans for critical supplier failure or port congestion. This planning prevents panic during disruptions.
STEP 5: ITERATE AND OPTIMIZE. Establish a regular review cycle, quarterly at a minimum. Analyze your metric performance, gather team feedback, and pilot new improvements. Treat your supply chain as a product that is constantly being refined.
## Technology Showdown: Key Tools for Modern Supply Chains
Modern technology is the engine of supply chain performance improvement. The market offers many solutions, but they serve different primary functions. The table below compares two major categories: Supply Chain Visibility Platforms and Advanced Planning Systems.
| Feature / Focus | Supply Chain Visibility Platform | Advanced Planning & Scheduling (APS) |
|---|---|---|
| PRIMARY GOAL | Real-time tracking and transparency across the entire chain. | Optimizing future plans for production, inventory, and demand. |
| CORE FUNCTION | Aggregates data from sensors, GPS, and ERP systems to show where items are and predict arrivals. | Uses algorithms and AI to create optimal production schedules, inventory levels, and distribution plans. |
| KEY BENEFIT | Enables proactive problem-solving (e.g., rerouting a delayed shipment). Improves customer communication. | Maximizes resource utilization, minimizes costs, and improves service levels through better planning. |
| BEST FOR SOLVING | Questions like “Where is my order?” and “Will it arrive on time?” | Questions like “How much should we produce next month?” and “Where should we stock inventory?” |
Choosing the right tool depends on your biggest challenge. Lack of visibility leads to firefighting, while poor planning leads to chronic inefficiency. Many leading companies eventually integrate both types of systems for a complete picture.
## Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
WARNING: AVOIDING THESE MISTAKES CAN SAVE YOU SIGNIFICANT TIME AND RESOURCES.
A frequent mistake is focusing solely on cost reduction. While important, cutting costs in transportation or inventory can backfire by increasing stockouts or slowing delivery times, ultimately hurting revenue and customer loyalty. Always balance cost metrics with service and quality metrics.
Another major pitfall is neglecting supplier relationships. Treating suppliers as purely transactional partners undermines resilience. When disruptions hit, strong relationships ensure you are a priority. Invest in collaborative planning and fair communication with your key suppliers.
Finally, do not underestimate data quality. Implementing advanced analytics on poor, siloed, or outdated data leads to faulty insights and bad decisions. Any technology initiative must start with a foundation of clean, integrated data. According to a 2023 Gartner report, poor data quality is responsible for an average of $15 million per year in losses for organizations (来源: Gartner).
## The Future of Supply Chain Performance
The future is intelligent, autonomous, and sustainable. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are moving beyond planning into predictive problem-solving, anticipating disruptions before they occur. The Internet of Things provides a constant stream of real-time data from pallets, vehicles, and warehouse shelves.
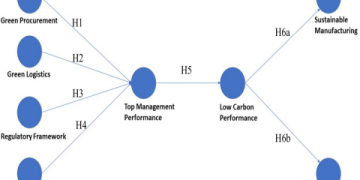
Furthermore, sustainability is now a core component of supply chain performance. Consumers and investors demand transparency into carbon footprints and ethical sourcing. Companies that build circular economy principles and green logistics into their operations will see regulatory, cost, and brand benefits. Our team has observed that clients leading in sustainability reporting often discover unexpected operational efficiencies, turning a compliance cost into a value driver.
## Your Actionable Performance Checklist
Use this checklist to start or refine your supply chain performance journey. Do not just read it. Assign owners and deadlines for each action item.
IDENTIFY AND TRACK YOUR TOP FIVE METRICS. Select the most relevant metrics from section two. Establish a baseline and set quarterly improvement targets.
CONDUCT A SUPPLIER RISK ASSESSMENT. Categorize your top 10 suppliers by criticality and risk. For high-risk critical suppliers, develop a backup plan.
AUDIT INTERNAL DATA QUALITY AND FLOW. Choose one critical process, like order-to-cash, and map how data moves between departments. Identify and fix one key data gap or error point.
IMPLEMENT ONE PILOT VISIBILITY PROJECT. Select a high-value shipment lane or product line. Implement basic real-time tracking and share the status dashboard with the relevant sales and customer service teams.
SCHEDULE A QUARTERLY PERFORMANCE REVIEW. Bring together leaders from procurement, logistics, sales, and finance. Review metrics, discuss disruptions, and agree on one strategic improvement for the next quarter.
By systematically working through these areas, you will build a supply chain that is not only efficient but also agile and resilient. The work to improve supply chain performance is continuous, but the rewards in customer loyalty, cost savings, and market advantage are substantial and lasting.