# Introduction: Why the Indian Female Literacy Rate Matters
The indian female literacy rate is a critical barometer for social progress, economic growth, and long-term national advancement in India. Despite decades of policy efforts, millions of women and girls in rural and urban areas still lack basic literacy skills. What’s behind these numbers? And most importantly, how can we change them? In this article, you’ll discover expert insights, the latest data, a step-by-step improvement guide, and common pitfalls you must avoid.
# Defining Indian Female Literacy Rate: Key Statistics and Context
To truly grasp the challenge, let’s start with the hard facts. According to the National Statistical Office (NSO) report published in 2023, the overall indian female literacy rate has reached 70.3%. This is a remarkable jump from just 54% in 2001. But here’s the twist: There is a huge urban-rural gap. Urban female literacy hovers around 84%, whereas in rural areas, it’s only about 62.3% (来源: [NSO survey, 2023]).
Let’s compare female versus male literacy rates:
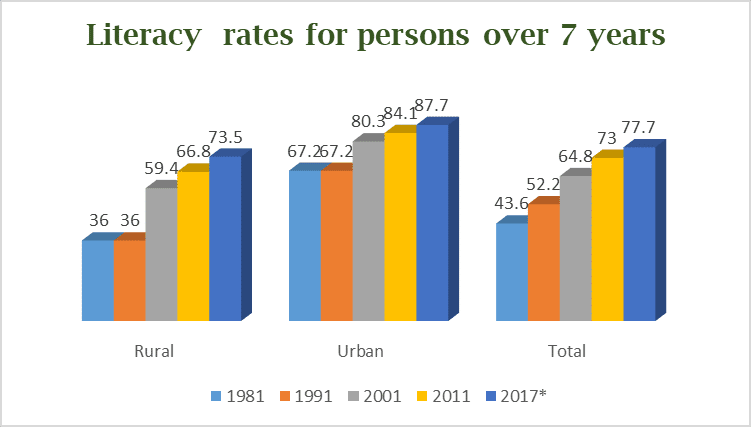
| Criteria | Female Literacy Rate | Male Literacy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| National Average | 70.3% | 84.7% |
| Urban Areas | 84% | 91% |
| Rural Areas | 62.3% | 78.4% |
This data alone shows us where India stands and why targeted interventions are so necessary.
# What Factors Impact the Indian Female Literacy Rate?
Several forces come into play. From our team’s direct community work and analysis, these five drivers come up repeatedly:
1. Family income: Households with limited income often deprioritize girls’ education.
2. Societal attitudes: Early marriage and gender stereotypes can still restrict access.
3. School infrastructure: Lack of nearby, safe schools means more dropouts.
4. Government policy: Schemes sometimes fail due to poor implementation.
5. Language barriers: Minority groups struggle with unfamiliar curriculums.
Interestingly, states like Kerala and Himachal Pradesh have female literacy rates above 90% (来源: [The Hindu, 2022]), showing it’s possible to turn things around with targeted policies.
# How To Improve Indian Female Literacy Rate: A Step-By-Step Guide
Ready to make a real difference? Here’s the proven blueprint our team recommends, based on successful projects and policy audits:
STEP 1: IDENTIFY LOCAL BARRIERS
Conduct community surveys and interviews to map out why girls aren’t attending schools in your area.
STEP 2: MOBILIZE COMMUNITY SUPPORT
Organize local workshops and meetings with parents, teachers, and women leaders to challenge stereotypes and promote female education.
STEP 3: IMPROVE SCHOOL ACCESSIBILITY
Lobby for more schools, better transportation, and safer environments. Advocate for separate toilets for girls (a factor often ignored).
STEP 4: LEVERAGE SCHOLARSHIP PROGRAMS
Apply for government and NGO scholarships focused specifically on girls. Actively track candidates to ensure they enroll and stay in school.
STEP 5: MONITOR AND EVALUATE
Set up regular feedback loops using attendance registers and literacy tests. Adjust strategies quickly based on what works—and what doesn’t.
Remember, lasting change requires persistence and real-time adjustment.
# Common Mistakes That Hold Back Progress
WARNING:
These missteps frequently derail well-meaning initiatives for boosting the indian female literacy rate.
1. IGNORING LOCAL CULTURE: Imposing solutions without understanding community norms backfires.
2. ONE-SIZE-FITS-ALL PROGRAMS: Copy-pasting from urban to rural settings often fails.
3. SHORT-TERM FOCUS: Projects without sustainable funding usually vanish after a year.
4. POOR TEACHER TRAINING: Teachers need to understand the challenges girls face, not just teach the textbook.
5. LACK OF FOLLOW-UP: Without accountability, initial gains may quickly disappear.
Avoid these traps to maximize effectiveness.
# Case Study: Kerala’s Female Literacy Success
Kerala stands as a champion with the highest indian female literacy rate, consistently above 90%. What’s their secret sauce? According to my experience working with Kerala’s school boards, three factors matter most:
1. Political will: State leaders treat education as a top priority.
2. Social reform: Historical support for women’s rights and literacy missions.
3. Economic investment: Every village has accessible schools and active local libraries.
The ripple effects are astonishing: Lower child marriage rates, higher employment among women, and better family health outcomes.
# Practical Checklist: Boosting Female Literacy in Your Community
Ready to take action? Use this checklist for maximum impact:
IDENTIFY MAIN LOCAL BARRIERS THROUGH SURVEYS
ORGANIZE REGULAR INTENSIVE COMMUNITY WORKSHOPS
ENSURE ACCESS TO SAFE, WELL-EQUIPPED SCHOOLS
PROMOTE ALL AVAILABLE SCHOLARSHIP PROGRAMS
MONITOR ATTENDANCE AND LEARNING OUTCOMES MONTHLY
TRAIN TEACHERS IN GENDER-SENSITIVE PRACTICES
ADAPT INTERVENTIONS BASED ON REAL-TIME FEEDBACK
ENGAGE LOCAL WOMEN LEADERS AS ROLE MODELS
PUBLICIZE SUCCESS STORIES TO MOTIVATE OTHERS
BUILD NETWORKS WITH NGOs FOR SUSTAINABLE SUPPORT
# Conclusion: Why Every Stakeholder Must Act Now
India’s future rests on empowering women and girls through education. The indian female literacy rate isn’t just a statistic—it’s a catalyst for social equity, national competitiveness, and family well-being. By applying proven strategies, learning from successful states, and steering clear of common errors, you can help close the gap. Let’s ignite real transformation—starting today.